According to the American Cancer Society, colorectal cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths in the United States. However, early diagnosis often leads to a complete cure. Almost all colon cancer starts in glands in the lining of the colon and rectum. When doctors talk about colorectal cancer, this is usually what they are talking about. There is no single cause of colon cancer. Nearly all colon cancers begin as noncancerous (benign) polyps, which slowly develop into cancer.
What you eat may play a role in your risk of colon cancer. Colon cancer may be associated with a high-fat, low-fiber diet and red meat. However, some studies have found that the risk does not drop if you switch to a high-fiber diet, so this link is not yet clear. Smoking cigarettes and drinking alcohol are other risk factors for colorectal cancer.
Stage 0 colon cancer may be treated by removing the cancer cells, often during a colonoscopy. For stages I, II, and III cancer, more extensive surgery is needed to remove the part of the colon that is cancerous.
SAlmost all patients with stage III colon cancer should receive chemotherapy after surgery for approximately 6 - 8 months. The chemotherapy drug 5-fluorouracil has been shown to increase the chance of a cure in certain patients. Chemotherapy is also used to improve symptoms and prolong survival in patients with stage IV colon cancer.
You may receive just one type, or a combination of these drugs.
Although radiation therapy is occasionally used in patients with colon cancer, it is usually used in combination with chemotherapy for patients with stage III rectal cancer.
SAlmost all patients with stage III colon cancer should receive chemotherapy after surgery for approximately 6 - 8 months. The chemotherapy drug 5-fluorouracil has been shown to increase the chance of a cure in certain patients.
SAlmost all patients with stage III colon cancer should receive chemotherapy after surgery for approximately 6 - 8 months. The chemotherapy drug 5-fluorouracil has been shown to increase the chance of a cure in certain patients.
With proper screening, colon cancer can be detected before symptoms develop, when it is most curable. Your doctor will perform a physical exam and press on your belly area. The physical exam rarely shows any problems, although the doctor may feel a lump (mass) in the abdomen. A rectal exam may reveal a mass in patients with rectal cancer, but not colon cancer. A fecal occult blood test (FOBT) may detect small amounts of blood in the stool, which could suggest colon cancer. However, this test is often negative in patients with colon cancer. For this reason, a FOBT must be done along with colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy. It is also important to note that a positive FOBT doesn't necessarily mean you have cancer.
Note: Only colonoscopy can see the entire colon, and this is the best screening test for colon cancer.
If your doctor learns that you do have colorectal cancer, more tests will be done to see if the cancer has spread. This is called staging. CT or MRI scans of the abdomen, pelvic area, chest, or brain may be used to stage the cancer. Sometimes, PET scans are also used.
Colon, or colorectal, cancer is cancer that starts in the large intestine (colon) or the rectum (end of the colon).
Blood tests to detect tumor markers, including carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and CA 19-9, may help your physician follow you during and after treatment.
Colon cancer is, in many cases, a treatable disease if it is caught early. How well you do depends on many things, including the stage of the cancer. In general, when they are treated at an early stage, many patients survive at least 5 years after their diagnosis. (This is called the 5-year survival rate.) If the colon cancer does not come back (recur) within 5 years, it is considered cured. Stage I, II, and III cancers are considered potentially curable. In most cases, stage IV cancer is not considered curable, although there are exceptions.
The death rate for colon cancer has dropped in the last 15 years. This may be due to increased awareness and screening by colonoscopy. Colon cancer can almost always be caught by colonoscopy in its earliest and most curable stages. Almost all men and women age 50 and older should have a colon cancer screening. Patients at risk may need earlier screening. Colon cancer screening can often find polyps before they become cancerous. Removing these polyps may prevent colon cancer. Changing your diet and lifestyle is important. Some evidence suggests that low-fat and high-fiber diets may reduce your risk of colon cancer.
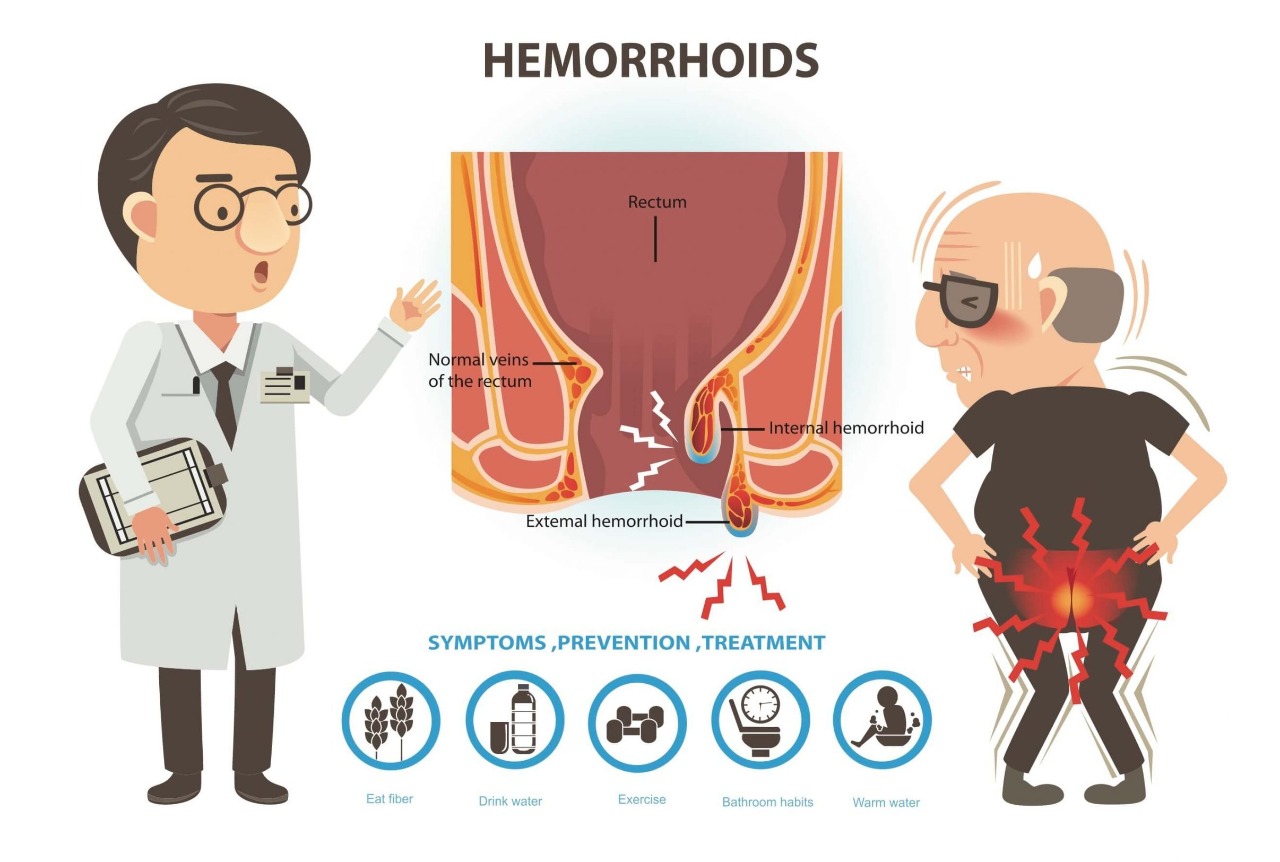
Haemorrhoids, also known as piles, are natural cushions of tissue and veins located at the junction of rectum and anus.
Read More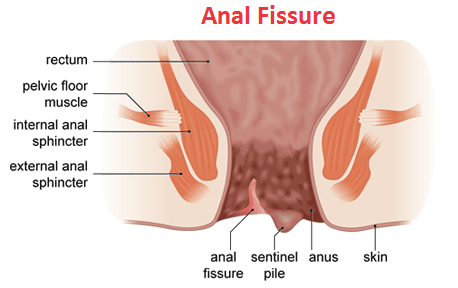
Per rectal examination is painful due to Spasm of internal sphincter, A split or cut on the posterior or anterior midline of the anal verge.
Read More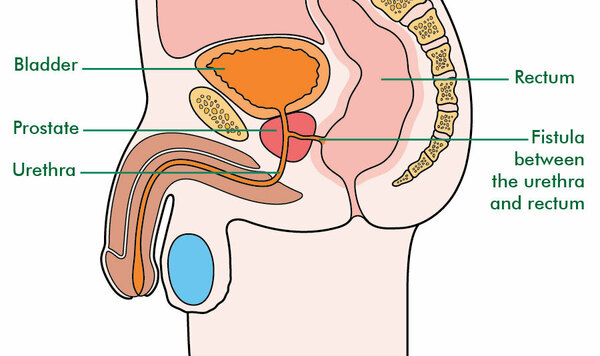
A fistula in ano is a hollow tract lined with granulation tissue connecting a primary opening inside the anal canal to a secondary opening in the peri anal skin.
Read More